Service organizations bear a great responsibility when working with clients to fulfill service needs while ensuring protection of certain aspects of the client’s business.
SOC 1 & SOC 2 Audits Require Manual Testing by a Qualified Auditor
For the Type 2 portion of both the SOC 1 and the SOC 2 audits, walkthroughs and testing of the controls set up at the service organization. Testing is crucial to Type II engagements to give the auditor more information to form an opinion on the suitability of the design, as well as the operating effectiveness of controls during the specified period under review.
During either SOC Type 2 audit, the auditor walks through and tests each control objective or criteria with a specific type of testing method or procedure.
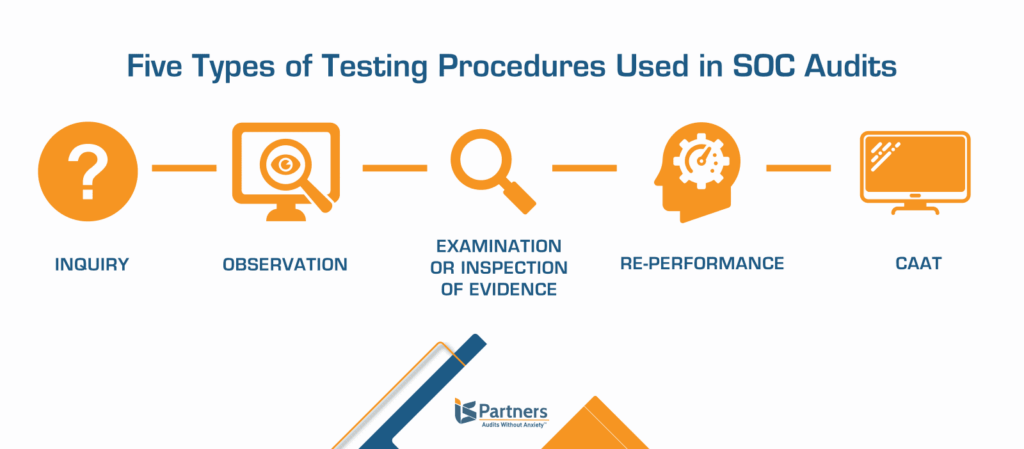
5 Testing Methods Used During Audit Procedures
There are five core testing methods that auditors use to confirm the facts and answers that a business wants to attain during an audit. The nature of these test methods focuses on everything from asking probing questions to inspecting documents and re-performing calculations.
Each testing method helps the auditor issue a well-informed opinion, based on evidence. Further, it provides the auditor with the information needed to provide qualified conclusions, whether the business is operating optimally, and managing risks properly.
These are the five types of testing methods used during audits.
- Inquiry
- Observation
- Examination or Inspection of Evidence
- Re-performance
- Computer Assisted Audit Technique (CAAT)
Inquiry
Inquiry is a fairly straightforward testing method, using interview-style questioning with the point of contact for certain controls. Because the quality of the information gained from inquiry depends on the accuracy and truthfulness of the interviewee, it is considered a weaker form of evidence. With the inquiry method, auditors ask questions of the organization’s managers, accountants and any other key staff to help determine some relevant information. The auditor may ask about business processes and the appropriate recording of financial transactions to make sure the company is doing everything possible to avoid risks.
One example of inquiry commonly used is asking the business owner how the company’s financial and data security records are stored. The auditor takes the responses into account—but does not accept the answers alone as confirmation—to establish additional testing criteria since this method is often used in conjunction with other, more reliable methods.
Observation
Another simple, basic and effective testing method involves an auditor’s observation of tasks, procedures and conditions. This testing method is most often used when there is no documentation of the operation of a control.
Traditionally, observation has been performed on-site during the evidence-gather phase of a SOC audit. For example, management at an audited organization may state that certain noted records have been appropriately secured in a locked drawer. Then, in order to verify that certain stated records have been securely stored in locked cabinets, the auditor will watch an employee unlock the specified drawer during normal daily activities and take out the records.
“Nowadays, with remote auditing, we are also able to get on a videocall with an audit client and check the conditions of the environment or configuration virtually. And this is a valid testing method for SOC audit purposes.”
– Joe Ciancimino, CISA, CRISC, and director at I.S. Partners.
Observation, even done remotely, can ensure that a company has an air conditioning system capable of keeping their servers cool by checking the thermostat in the equipment room. Or, for example, we can observe the configuration of IT systems to make sure that requirements are met.
Examination or Inspection of Evidence
This testing method helps auditors determine whether manual controls are being consistently performed and properly documented. Inspection can be used to verify the implementation of control measures, and to test certain attributes of policies and procedures.
For example, an auditor may check to make sure that backups are scheduled to run on a regular basis or that data classification controls. In these cases, the auditor can use inspection to verify that the control has been designed and is operating effectively. He or she will check to see if forms are being filled out correctly. Examination of evidence also includes the review of written documentation and records that might include visitor logs, employee manuals and system databases.
Re-performance
Re-performance is used when inquiry, observation, and physical examination and inspection have failed to provide the requisite assurance that a control is operating effectively. It’s also the method that is used least frequently in the field. Re-performance requires the auditor to manually execute the control in question, such as re-performing a calculation that is usually automated. The auditor can leverage work done by an internal auditor and documented in work papers, so that only a sample of the work needs to be re-tested to verify.
The re-performance method is helpful in decreasing the workload for auditors and determining whether automated controls are operating effectively. It is the strongest type of testing to highlight the operating effectiveness of a control.
Computer-Assisted Audit Technique (CAAT)
The CAAT method of testing is often used to analyze large volumes of data or a sample of compiled data. Using special software, CAAT testing runs a script over a ledger, spreadsheet, or an entire database, to spot trends, irregularities, and potentially fraudulent entries.
“I.S. Partners doesn’t use CAAT methods very often. The automated process can be helpful when we need to weed through big numbers and a large of data. The computer-aided testing helps us focus in on areas where there are statistical irregularities, but from that point forward, the testing needs to be done by a skilled auditor to meet due diligence,” explains Joe.
How Do SOC Auditors Determine Which Testing Method to Use?
The way that controls are tested for a SOC audit is always situation-based, according to Joe. Usually, the nature of the control determines how we test. For example, firewalls are always observed; that’s just how they need to be tested.
“Inquiry is always a part of the testing process too; it just naturally happens, but we wouldn’t consider the information reliable enough to take it at face value. Whenever inquiry alone is the testing method, it should be considered a deficiency. The information is not very substantial” That’s why auditors working for credible firms—like I.S. Partners—always try to back up these weaker testing methods with another type of evidence.
How Has SOC Testing Changed in Keeping with Technology?
One recent development in our field is the move towards automation of the auditing process. Auditors have been largely responding to this increased demand. Automation has valuable advantages for audited entities because it can streamline evidence collection and make auditing smoother.
“But what a lot of startups and companies that are new to compliance don’t always understand is that SOC testing and reporting really require a certified auditor. This is a huge issue in the market currently…Vanta, and automated audit tools like that, don’t do testing. Plus, what the tools tells you what to expect may not be what the auditor will ask of you during the actual audit. There’s a lot of due diligence that still needs to be done even if you sign up with one of these tools. Automated tools might be helpful for audit preparation, if an organization has an internal person who knows what he/she is doing. But to actually pass a SOC audit, the company needs to be able to describe controls or functions of your environment in detail which can present major challenges if your organization doesn’t have that information on hand. There is no cookie-cutter approach; passing an audit requires real monitoring and a real control environment,” explains Joe.
Another new development is the migration to cloud computing. “As our clients rely more heavily on cloud environments, the amount of testing related to physical access has largely decreased. As the responsibility for physical access shifts to CSPs, our clients can focus more on vendor monitoring. We remind our clients that they are still responsible for their data stored in the cloud and help them set up reliable ways of monitoring their third-party cloud vendors.”
Preparing for SOC Certification? | I.S. Partners Can Help
“The best approach is having a dedicated individual in your organization to lead audit and compliance efforts and also working with a human being. Work with an auditor who will actually take the time to go through everything with you and make sure that you are set up and ready for an audit.”
Do you need more information about any of the five test methods? Maybe you need some guidance on choosing the right method, or methods, for your organization. Our auditing team at I.S. Partners, LLC. is here and happy to clarify this important aspect of your upcoming audit.
We ensure that the audit testing procedures comply with the guidelines laid out by the AICPA, which means the tests confirm design and operating effectiveness.