According to the FBI’s annual Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), there were 8,47,376 cybercrime complaints in 2021. The total cost of cybercrime in 2121 was $6.9 billion. The complaints have been increasing every year as cybercriminals are using new, more sophisticated methods for malicious attacks.
To keep one step ahead of cybercrime, the regulatory landscape is also rapidly evolving. Going forward, many industries can expect more data security regulations. But one industry where the tolerance for cybercrime is extremely low is Defense. Due to the sensitive information, a security breach cannot just be quantified in monetary losses – it could be a threat to national security.
This is why, all DoD organizations require that any business entity in their supply chain must comply with a certain level of security standards. The main purpose of introducing CMMC was to have a standardized framework in place for robust cybersecurity.
In this guide, we will cover everything you need to know about CMMC.
What Is CMMC?
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) represents a program under the US Department of Defense (DoD) and is applicable to all defense contractors. CMMC was introduced to ensure that all defense contractors meet a certain level of cybersecurity maturity. It is designed to protect the Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) throughout the Defense Industrial Base (DIB).
CMMC 1.0 was introduced in January 2020. It had 5 levels of certifications that can be loosely described as below.
Level 1 – Foundational cyber hygiene
Level 2 – Intermediate cyber hygiene
Level 3 – Good cyber hygiene
Level 4 – Proactive cyber hygiene
Level 5 – Advanced/Progressive cyber hygiene
CMMC has evolved since 2020 but the core idea remains the same. In November 2021, CMMC 2.0 was introduced. CMMC 2.0 has several amendments. The most notable change is that the 5 levels of certification are streamlined into 3 levels. These are as given below.
Level 1 – Foundational cyber hygiene with basic safeguarding measures expected. This level is expected from DoD contractors that deal with FCI.
Level 2 – Advanced cyber hygiene aligned with NIST. This level is expected from DoD contractors that deal with CUI.
Level 3 – Expert cyber hygiene aligned with NIST. This level is expected from DoD contractors that deal with the highest priority programs with CUI.
Apart from the change in the CMMC levels, the new model relies heavily on self-assessments. Thus, DoD contractors can assess and manage their cybersecurity hygiene themselves. Key objectives of CMMC 2.0 include focusing on risk, increasing cost-effectiveness, and ensuring wider accessibility, making compliance easier for both small and large businesses.
How Does CMMC Relate to NIST?
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) provides the baseline requirements for data protection. CMMC 2.0 incorporates those standards to define a more structured certification model with different levels, third-party audits, and additional requirements specific to DoD contractors.
CMMC 2.0 requirements are based on the NIST guidelines, more specifically on the NIST Special Publication 800-171.
How Long Does CMMC Certification Last?
Once an organization gets certified under CMMC 2.0, the certification is valid for three years. This is to ensure that the certified organization keeps up with the evolving standards as well as the threat landscape. After three years, the organization will need to go through the assessment and certification process again if they wish to continue working on DoD projects. However, do note that ongoing compliance is necessary during the three-year period.
Who Needs to Comply With CMMC?
CMMC program applies to any individuals or organizations that directly or indirectly work with the U.S. DoD. This includes defense contractors and subcontractors in the DoD supply chain. Since the DoD supply chain is quite extensive, here are examples of some of the industries that need to be compliant with CMMC.
- Aerospace: Organizations involved in the development and manufacturing of aircraft, space vehicles, and related equipment and spare parts used by the defense sector.
- Defense equipment: Businesses that manufacture defense equipment, weapons, vehicles, hardware, etc. used in defense-related products or offer related services.
- IT Services: Companies that provide IT services to DoD organizations including IT infrastructure maintenance and support, cybersecurity, network support, etc.
- Research & development: Organizations involved in the R&D of new defense-related technologies or products.
- Education: An educational institution that is involved in defense-related research, training, or educational services under DoD contracts.
- Professional services: Any organization that provides services such as consulting, engineering, logistics, and administration.
Is CMMC 2.0 Applicable Currently?
All DoD contractors are expected to comply with the appropriate level of CMMC 2.0 by October 2025. (Date subject to change).
Even though CMMC 2.0 compliance is not mandatory at the moment, organizations looking to get themselves certified should start preparing now itself. Due to the extensive nature of the compliance requirements, it’s a good idea to start understanding and implementing the requirements.
Who Issues the CMMC Certification?
An accredited CMMC Third-Party Assessor Organization (C3PAO) assesses whether an organization has implemented the necessary controls as required by the certification level. The C3PAO sends a report to the CMMC Accreditation Body (CMMC-AB) for review. The final decision about issuing the certification lies with CMMC-AB.
For CMMC 2.0, it is expected that for Level 1 certifications, self-assessment by the organization would be sufficient. Self-assessments would also be sufficient for a subset of Level 2 certifications. For the rest of the Level 2 certifications and all of the Level 3 certifications, third-party assessment would be required. Also, for Level 3 certifications, an assessment carried out by government officials would be required. All these assessments would be triennial to ensure that the compliance is relevant.
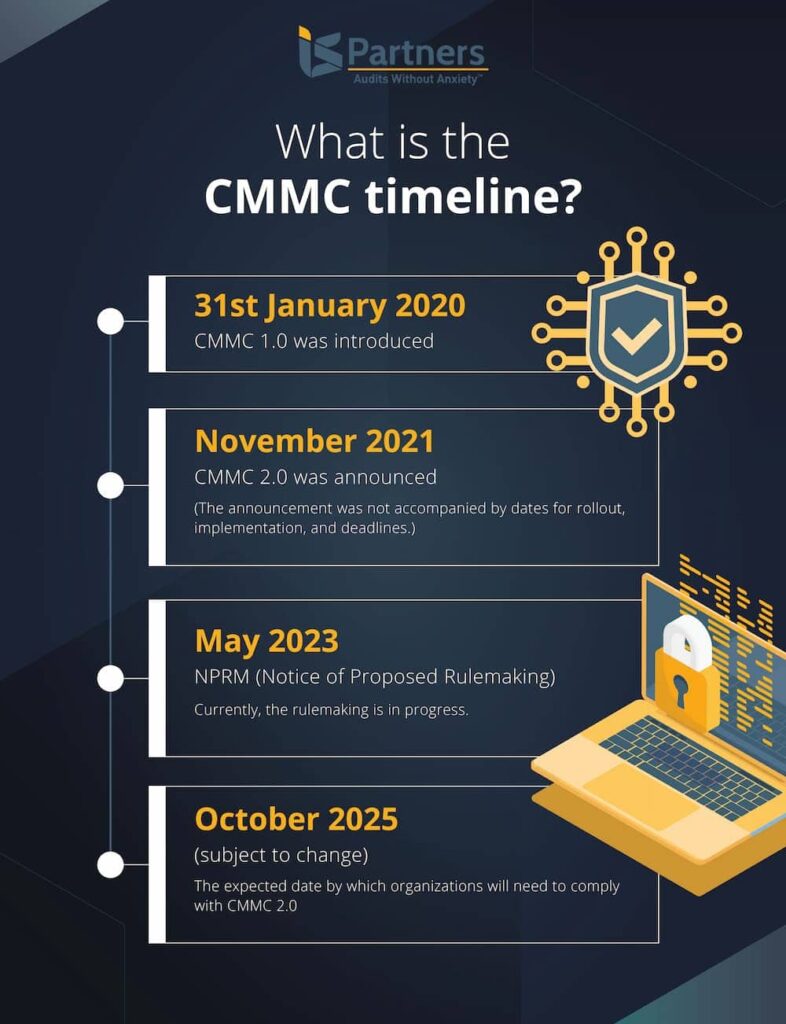
What Is the CMMC Timeline?
- CMMC 1.0 was introduced on 31st January 2020.
- CMMC 2.0 was announced in November 2021. However, the announcement was not accompanied by dates for rollout, implementation, and deadlines.
- NPRM (Notice of Proposed Rulemaking) was announced in May 2023.
- Currently, the rulemaking is in progress.
- The expected date by which organizations will need to comply with CMMC 2.0 is October 2025 (subject to change).
What Is the Interim Rule of CMMC?
During the interim period, i.e. till the time CMMC 2.0 would be officially rolled out, organizations can go for CMMC 1.0 certification. Once CMMC 2.0 is codified, the organizations would need to comply with the new rules within the specified deadline.
According to the interim rule of CMMC, all DoD contractors must conduct a cybersecurity self-assessment and assess whether they have implemented all 110 rules as defined in NIST SP 800-171. This assessment needs to be scored – one point for each implemented control and the highest score of 110. Each control not being implemented or implemented only partially would deduct a point.
When the score is less than 110, DoD contractors need to document a plan to implement the remaining controls in a POA&M (Plan of Action & Milestones). The POA&M would be a living document, constantly updated with details of new controls being implemented and their effectiveness.
The key elements of POA&M include:
- Information about the cybersecurity risk due to the absence of a control or the partial implementation of a control
- Severity of each of the cybersecurity risks identified
- A plan to manage the cybersecurity risks by eliminating it completely or mitigating it
- A cost estimate of managing the cybersecurity risk
- A real-time documentation of the status of each risk
The POA&M should be immediately available upon request from any government authority.
What Is the Deadline for CMMC Compliance?
While the deadline for CMMC 2.0 implementation has not yet been declared, the time is right for organizations to start preparing for CMMC 2.0. By understanding more about the certification and starting with improving cybersecurity as per the CMMC guidelines, organizations can hope to get certified sooner, once CMMC 2.0 is officially rolled out. Since the eligibility to bid on DoD contracts is tied to CMMC certification, an early certification can make a lot of difference to your chances of winning a bid.
How Much Does CMMC Cost?
The current cost of CMMC 1.0 depends on several factors. The main factors are:
- Size of the organization
- The complexity of the organization
- Level of certification required
- Fees charged by C3PAO
- Any costs incurred for implementing the required controls
- Costs incurred for procuring technology and personnel to implement controls
The fees charged by C3PAO can vary. Hence, it’s a good idea to get quotes from multiple third-party assessors and choose based on the cost as well as the services offered.
Regarding CMMC 2.0, the DoD plans to release a comprehensive cost analysis for each level of CMMC 2.0 as part of rulemaking. However, it is currently anticipated that the costs for CMMC 2.0 will be significantly lower when compared to CMMC 1.0.
CMMC Level 1 certification is based on self-assessment. Assuming that an organization has a good cybersecurity posture, CMMC Level 1 certification will incur a nominal cost. Level 2 and Level 3 certifications would need a more thorough process since these levels are associated with protecting CUI. A rough estimate of the cost of CMMC Level 2 and Level 3 certification suggests that it can range from $18,000 to $400,000, sometimes even more.
What Are the Benefits of CMMC?
CMMC certification has several benefits summarized below.
- Improved cybersecurity: Getting CMMC certified involves implementing cybersecurity controls. This improves the cybersecurity posture by establishing cybersecurity best practices and stringent controls.
- Competitive edge: Being CMMC certified gives you an advantage over your competitors by positioning you as an organization that takes cybersecurity seriously.
- Eligibility for DoD contracts: Since most DoD contracts need a CMMC certification, your business is eligible to bid for a contract if you are CMMC certified.
- Improved customer confidence: In the current times of rampant cybercrime, CMMC certification helps improve customer trust.
- Regulatory compliance: Complying with CMMC can align your organization with the ever-changing regulatory environment.
CMMC Compliance Checklist
Complying with CMMC requires a systematic approach. Here is a 12-step CMMC checklist to provide a clear path toward CMMC compliance.
- Identify your CMMC compliance level: Your required CMMC level depends on the type of government data you handle/will handle. Every defense contractor will need at least Level 1 compliance. If your organization handles CUI, it may require either CMMC Level 2 or Level 3.
- Assign ownership: CMMC compliance involves a lot of groundwork and ongoing effort. Assigning ownership to team member(s) helps in better adherence to policies and protocols to cover all bases.
- Optimize CUI interaction: The cost of compliance can depend on how CUI interacts with your environment. Figure out all the points where your environment comes in touch with CUI – from the time that it enters your systems, is stored/used, and exits the systems. Then, try to reduce the interaction of CUI so that the scope of CMMC reduces.
- Limit CUI access: Reduce the number of people that have access to CUI. This will reduce the unnecessary overheads in compliance by reducing training needs, cost of licenses, etc.
- Choose the right technologies for CUI Protection: You might have to use new technologies to ensure CMMC compliance. For example, if you use O365 or the GSuite, you might have to switch since these are not CMMC compliant.
- Take help from an expert: This is not a mandatory point on your checklist. However, if CMMC compliance seems too complex, an expert such as a CMMC registered practitioner can help streamline all processes toward compliance efforts.
- Prepare and maintain documentation: Some of the Level 2 and all of the Level 3 certification requirements would be validated by a third-party assessor. Hence, just having all compliance practices in place is not enough – you need to prepare and maintain documentation. You will need a System Security Plan (SSP) detailing the use of security controls.
- Plan for updates and upgrades: It’s possible that you might not be able to implement all 110 controls as per NIST SP 800-171. Creating a Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M) can help you plan for upgrades in technology and resources to implement the controls. C3PAOs will allow for some low-severity controls to be included in POA&M. However, POA&M is timebound and you will have to take action within 180 days of your assessment.
- Conduct a self-assessment: A self-assessment is a good way to find out where you stand in terms of CMMC compliance. You can then identify gaps and areas that need more work. You can use the SSP created as a reference to carry out the self-assessment.
- Close security gaps: Identify and close security gaps – most of the gaps would be revealed during the self-assessment.
- Schedule a C3PAO assessment: Choose a C3PAO based on the cost and services they provide and schedule time for the assessment.
CMMC Compliance Requirements
There are certain CMMC compliance requirements for each level.
Level 1 includes 17 security controls under 6 domains. The 6 domains are:
- Access control
- Identification and authentication
- Media protection
- Physical protection
- System and communication protections
- System and information integrity
Level 2 compliance includes 110 controls grouped under 14 domains. The 14 domains include the 6 domains mentioned above. The additional 8 domains are:
- Awareness training
- Configuration management
- Incident response
- Maintenance
- Personnel security
- Risk assessment
- Security assessment
- Audit and accountability
Level 3 CMMC compliance requires 130 controls grouped under 16 domains as well as those under Level 1 and Level 2. The additional 2 domains are:
- Recovery
- Situational awareness
Please note that even if the domains included in each compliance requirement overlap, the controls under each domain are different for different levels.
How to Get Started With CMMC Certification?
Here are the steps to start your efforts for CMMC compliance and certification.
- Understand and choose the appropriate CMMC Level.
- Identify the FCI and CUI data that you will be handling as part of your engagement as a DoD contractor.
- Thoroughly read the CMMC guides and appendices. Also read about NIST SP 800-53, ISO 27001, FISMA, etc.
- Conduct a gap assessment to identify gaps as per the CMMC and NIST guidelines.
- Create and review plans for bridging the gaps identified.
This is a good starting point to move toward CMMC certification. Starting the preparation now can boost your chances of getting CMMC certified without any hassles. Once CMMC 2.0 becomes mandatory, there will be a rush of organizations trying to get certified. Preparing now will give you an advantage over others who might wait till the rollout is official.
How to Become CMMC Compliant With I.S. Partners?
Getting CMMC certified is a step forward in adhering to the DoD requirements and getting ready to handle DoD projects. However, the process is time-consuming and effort-intensive – especially if you are a complex organization and/or going for CMMC for the first time. The CMMC framework is itself quite new and there are several unanswered questions.
I.S. Partners has a team of experts who help take the complexity away from CMMC compliance and certifications. With a deep understanding of compliance requirements and years of experience in managing compliance requirements for various standards, I.S. Partners helps in streamlining your efforts for CMMC certification.
I.S. Partners takes stock of your compliance posture and performs a gap assessment to identify improvement areas. The experts also help with creating and updating robust documentation including plans, policies, and process documents. Learn more about how I.S. Partners can help you with CMMC assessments and audits.