Key Takeaways
1. Cybersecurity compliance involves adhering to standards and regulations to protect sensitive information.
2. Following cybersecurity compliance frameworks improves your security posture, helps meet industry regulations, and boosts your reputation.
3. Understanding the required cybersecurity framework can be complex, but IS Partners offers tailored solutions to meet your specific needs.
What Is Cybersecurity Compliance?
Cybersecurity compliance refers to an organization’s adherence to laws, regulations, and standards regarding data security and privacy. It involves implementing security controls and best practices to safeguard sensitive data and maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets.
Compliance helps organizations mitigate legal and financial risks associated with non-compliance. It is crucial because it builds a solid security foundation, promotes best practices, and guides organizations in developing a thorough security program. It signals an organization’s commitment to secure business practices, minimizes the chances of data breaches, and helps build market reputation and customer trust.
How does it do that?
Compliance with necessary cybersecurity standards means your key systems and procedures are secure when handling sensitive data. When you follow these best practices, you can significantly reduce the chance of errors in your processes.
Significance of Cybersecurity Compliance
Cybersecurity compliance is important because it helps protect your business from financial losses, security breaches, and damage to your reputation. The compliance frameworks provide a common language everyone can understand, from the server room to the boardroom.
Cybersecurity compliance is not a one-time checkbox but an ongoing process. Organizations must continuously monitor their compliance posture, adapt to evolving regulations, and regularly train employees on security best practices. Investing in a robust compliance program is crucial for long-term business success and resilience against the ever-increasing threat of cyberattacks.
Here’s how these standards are used:
- Internal auditors and other stakeholders can evaluate the controls in place within their own organization.
- External auditors use them to assess and attest to the controls in an organization.
- Third parties (like potential customers and investors) use them to evaluate the risks of partnering with an organization.
Below, we describe the key contributions of cybersecurity compliance to service organizations:

Data Protection
Compliance with cybersecurity regulations and standards helps ensure that an organization is taking the necessary steps to safeguard sensitive information like customer data, financial records, and intellectual property from unauthorized access and breaches.
Risk Mitigation
Adhering to compliance requirements helps organizations identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and implement appropriate security controls. This proactive approach to threat management significantly reduces the chances of costly data breaches and cyberattacks.
Regulatory Obligations
Many industries have specific cybersecurity regulations that companies must follow, such as HIPAA in healthcare, PCI-DSS for payment card processing, and GDPR for data privacy. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines, legal consequences, and even suspension of operations.
Reputational Safeguard
Data breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust. By maintaining compliance, companies demonstrate their commitment to security best practices, which enhances their market standing and builds customer confidence.
Competitive Advantage
Comprehensive cybersecurity compliance can be a differentiating factor for businesses. Customers, particularly those concerned about data privacy, are more likely to choose a compliant company over less secure competitors.
Improved Data Management
Compliance requirements often involve keeping detailed records of data collection, storage, and access. This pushes organizations to streamline their data management practices, ultimately leading to better efficiency and decision-making.
Hence, maintaining cybersecurity compliance shows prospective partners in your industry that you’ve taken the necessary precautions to protect the customer information you gather.
Who Needs Cybersecurity Compliance?
Any organization handling data or operating with internet-exposed systems must take cybersecurity seriously. This includes almost every business, regardless of industry or size.
Some of the businesses that are commonly subject to cybersecurity compliance are:
- Healthcare Providers (Hospitals, Clinics)
- Financial Institutions (Banks, Credit unions)
- E-commerce and Retail (Online retailers, Payment processors)
- Government Agencies (Federal agencies, State and local government offices, Military departments)
- Educational Institutions (Universities, Colleges)
- Legal Services (Law firms, Legal consultancies)
- Manufacturing and Industrial (Factories, Industrial suppliers, Defense contractors)
- Technology Companies (Software developers, Cloud service providers)
- Telecommunications (Internet service providers, Mobile network operators, Data centers)
Remember that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility nowadays that impacts more than just your own company; it affects your clients, partners, and the broader digital community.
These days, Cybersecurity isn’t just a “nice-to-have” – it’s a “must-have” for everyone. Complying with cybersecurity requirements can be tough, especially when you have to meet different rules that sometimes conflict with each other.
It can be confusing to keep up with all the standards and regulations, and trying to do so can take up a lot of time and resources. This can leave gaps in your security. Dave Zuk, IS Partners’ Director for SOC Practice, shares his wisdom on this matter,
Cybersecurity frameworks are complex, with hundreds of controls and requirements. Some requirements and controls can be redundant and have to be tested multiple times if the audit/cybersecurity assessment time frames aren’t in sync.
One of the ways to effectively manage these challenges is by hiring a good audit firm with seasoned cybersecurity professionals. They will help alleviate the challenges by helping craft a business plan based on organizational needs, and identify and align controls and requirements to the highest standard for multiple compliance goals.
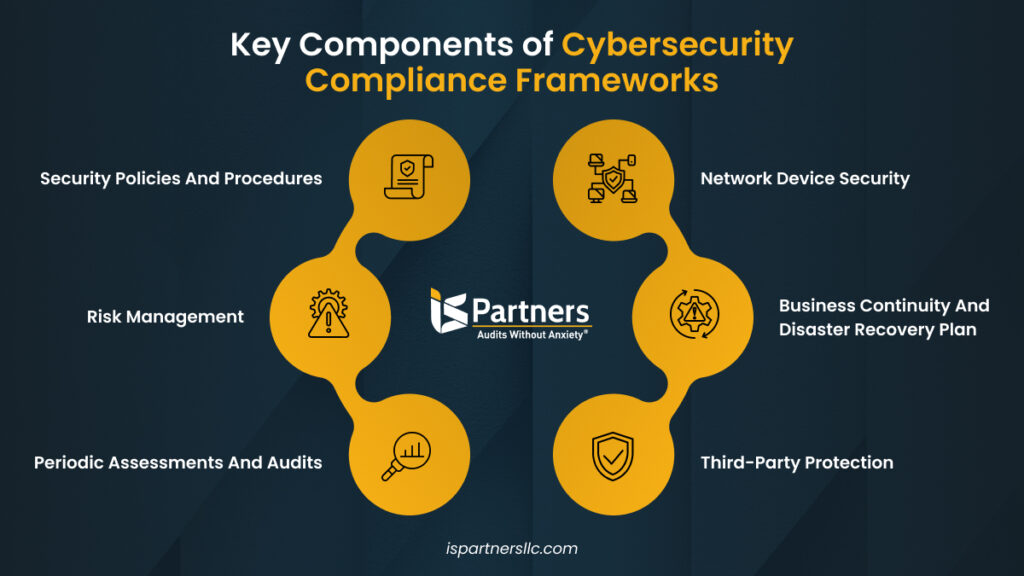
Key Components of Cybersecurity Compliance
The key components of cybersecurity compliance start with implementing the right security policies and procedures and having risk management strategies in place. All cybersecurity frameworks aim to protect information. While some of them vary in approach, several key frameworks often intersect in some aspects.
Below are some of the essential components of an effective cybersecurity compliance program.
Security Policies And Procedures
Cybersecurity policies set the standards for behavior, like encrypting email attachments and limiting social media use. These documents are detailed descriptions of how your company prepares for breaches and protects customer data from unauthorized access.
Risk Management
This involves systematically identifying, assessing, and prioritizing cybersecurity risks. The aim is to minimize, monitor, and control the likelihood or impact of unfortunate events.
Periodic Assessments And Audits
Regular evaluations and tests of an organization’s security controls, processes, and systems are essential to maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture.
Network Device Security
Both the physical and virtual components of your network infrastructure need attention, including firewalls, switches, access points, servers, virtual machines, remote access, VPN security, and encryption standards.
Business Continuity And Disaster Recovery Plan
These practices help an organization maintain operations after an adverse event. The goal is to limit risk and resume normal operations quickly, considering various unplanned events like natural disasters or human error.
Third-Party Protection
Also known as third-party risk management (TPRM), this involves practices, services, and technologies to identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity risks posed by external entities such as suppliers, service providers, and business partners.
Types of Cybersecurity Compliance
There are different types of cybersecurity compliance, and you can choose based on your industry type and cost implications. Each framework targets unique security aspects to protect data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Frameworks often target a specific aspect of data protection. For example, GDPR and HIPAA focus on privacy protection, while CMMC and NIST SP 800-171 are built to ensure safe supply chains. As such, it is essential to identify your needs to determine which type of cybersecurity compliance framework would work best.
Here are some of them:
SOC 2
SOC 2 is a voluntary security framework that guides organizations in protecting customer data from unauthorized access, security incidents, and other vulnerabilities.
Developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), SOC 2 compliance focuses on five trust service criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
The main goal of SOC 2 compliance is to ensure that third-party service providers handle and process client data securely, maintaining trust and reliability in their services.
PCI DSS
PCI compliance means adhering to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which is a set of requirements designed to ensure that all companies processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information or any cardholder data maintain a secure environment.
For example, banks, merchants, and service providers are held to higher standards due to the nature of their business.
If you’re part of an IT team, this compliance impacts you by requiring the enforcement of specific procedures and controls based on your PCI DSS level.
You need to complete self-assessment questionnaires, perform quarterly network scans, and undergo on-site independent security audits.
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an international standard for information security developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
ISO 27001 provides a framework for defining, implementing, operating, and improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
It is widely recognized as the leading standard for ensuring good information security practices.
HIPAA and HITECH
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a U.S. law that sets standards for protecting sensitive medical information.
Companies handling protected health information (PHI) need to implement and follow strict physical, network, and process security measures to comply with HIPAA regulations.
This includes covered entities like healthcare providers, payment processors, and operations staff, as well as business associates who access patient information to support treatment, payment, or operations.
Subcontractors and other related business associates must also comply with HIPAA standards. To further protect patient data, HITECH was developed.
The HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health) Act of 2009 was designed to promote the adoption of electronic health records (EHR) and supporting technology in the United States. It also aims to expand data breach notifications and enhance the protection of electronic protected health information (ePHI).
Wondering how to achieve HIPAA compliance? IS Partners has helped hundreds of companies achieve HIPAA certification with no hiccups. Get in touch to know more.
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the strictest privacy and security law in the world. GDPR specifies legally sanctioned methods for transferring and processing personal data, outlines the necessary protections for data at rest and in transit, and defines the rights of European Union residents regarding the collection, use, and ownership of their data.
It also provides a common language for a uniform understanding of security regulations. For example, it prevents companies from misleading consumers with confusing or vague language on their websites. GDPR requires that:
- Sites promptly inform visitors if their personal data is ever breached
- Website visitors are notified about the data being collected
- Visitors give explicit consent to data collection by clicking a button or taking another action
Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX)
The SOX is a federal law enacted in 2002 to protect the public from financial fraud and errors by businesses and financial institutions. It imposes various security requirements for applications and systems processing financial data.
This includes access management, general IT controls (ITGCs), and entity-level controls, which the compliance team often manages. This framework is mainly used by public companies or those planning an initial public offering (IPO).
CMMC
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) program sets up assessment mechanisms to verify that defense contractors comply with the Department of Defense (DoD) security requirements for protecting sensitive information.
Defense Industrial Base (DIB) contractors handle sensitive government data to develop and deliver goods and services, and CMMC ensures they secure identifiable information just as military departments and government agencies do.
Currently, CMMC applies only to DoD contractors, and the DoD is starting to require certification for certain contracts. In the future, CMMC may extend to all non-DoD government contractors as well.
FISMA
The Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) establishes a set of guidelines and security standards to protect government information and operations.
FISMA requires every federal agency to create, document, and implement a comprehensive information security program.
This program aims to safeguard sensitive data and information systems that support the agency’s operations and information assets, including those managed by other agencies, third-party vendors, or service providers.
How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Compliance Program?
The selection of a cybersecurity framework is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Several factors come into play, like the type of industry, cost, and business needs. In addition, a relevant and effective cybersecurity compliance program has established comprehensive and continuous monitoring for ongoing compliance.
Below, we breakdown the key things you need to consider when following a cybersecurity program.
Industry Requirements
Different industries have specific regulatory requirements. So you need to choose the that aligns with the standards and regulations of your industry.
For example, HIPAA is a cornerstone for healthcare cybersecurity and regulatory compliance. Hospitals, insurance companies, and healthcare providers must follow HIPAA compliance checklists to protect sensitive patient data.
Scope And Complexity
The next factor to consider is evaluating the framework’s scope and complexity. Some frameworks are more comprehensive and may be better suited for larger organizations, while others are more streamlined for smaller businesses.
Take PCI DSS, for instance. This framework is essential for any business that processes, stores or transmits credit card information, irrespective of whether your business is small or large. Usually, retailers, payment processors, and e-commerce sites rely on PCI DSS to secure customer payment data and prevent fraud.
Cost
Consider the cost of implementing and maintaining the framework. This includes not only the direct costs but also the resources required for ongoing compliance.
For example, let’s say a small e-commerce business is looking at SOC 2 compliance. SOC 2 Type 1 gives you a snapshot of your systems and controls at a specific moment, while SOC 2 Type 2 looks at how effective those controls are over a longer period.
Both types involve costs for auditing, compliance, and ongoing monitoring. However, SOC 2 Type 2 offers a more thorough and continuous evaluation, making it a great choice for businesses wanting strong, ongoing data protection.
Integration With Existing Systems
The framework should integrate smoothly with your current IT infrastructure and processes. This minimizes disruption and ensures a more seamless adoption process.
For example, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is known for its flexibility and adaptability, making it well-suited for integration with existing systems.
I.S Partner’s Role In Helping You Achieve Cybersecurity Compliance
Choosing the right cybersecurity framework is a crucial step in securing your organization’s digital assets. With cyberattacks on the rise and new data protection and cybersecurity laws emerging, staying ahead of the curve is essential. No one wants to risk data breaches that could harm both your business and your customers.
This is where IS Partners come in. We specialize in helping you achieve cybersecurity compliance with tailor-made solutions that fit your specific needs. Whether it’s international, federal, or state regulatory standards, we’ve got you covered.
We offer cybersecurity assessments, training, risk management, and advanced IT security audits to ensure your organization takes a proactive approach to cybersecurity compliance standards.
Our expertise ensures you’re always a step ahead in safeguarding your data.
Ready to get started? Reach out to us today.











